All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Frequency of Regulatory T Cells is Not Affected by Transient B Cell Depletion Using Anti-CD20 Antibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Objectives
Transient B cell depletion with the monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody rituximab has shown favourable clinical responses in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Recently a characteristic regeneration pattern of B cell subpopulations has been reported. However, little is known about the impact of B-cell depletion on peripheral T cells in particular regulatory T cells.
Materials and Methodology
17 patients with RA having failed anti-TNF were treated with rituximab. Four colour staining was performed using CD19, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD16, CD56, CD25, HLA-DR, HLA-G and intracellular Foxp3 at five time points spanning up to 12 months after rituximab. In addition, quantification of the soluble form of the HLA class I molecule HLA-G by ELISA has been performed.
Results
Peripheral B cell depletion lasted 6 to 9 months. The absolute number of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes showed no significant changes up to 1 year after B-cell depletion compared to before therapy. Only the relative frequency for CD3 and CD4 showed a significant increase (p < 0.05). In particular, CD4+CD25++ and Foxp3 positive regulatory T cells remained constant. The percentage of HLA-G positive cells in the CD4+ or CD8+ population did not change significantly either. The amount of sHLA-G remained without significant changes.
Conclusion
Absolute T cell counts showed no significant changes after rituximab compared to the time point before therapy.In particular, the frequency of regulatory T cells with a CD4+CD25++ phenotype as well as positive Foxp3 expression were numerically stable. Additionally, HLA-G positive regulatory T cells and soluble levels of HLA-G showed no significant changes.
INTRODUCTION
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) represents a chronic inflammatory disease leading to progressive cartilage and joint destruction. RA is treated with DMARDs (disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs) alone or in combination with glucocorticoids and/or so called biologicals, e.g. TNFalpha-antagonists. The introduction of TNFalpha blockers has revolutionized treatment of RA. Nevertheless, up to one third of by this means treated patients does not respond adequately [1]. Therefore there is still need for other treatment strategies like rituximab, a B-cell depleting anit-CD20 monoclonal antibody [2-4]. Within the last years growing evidence has emerged underlining the pathogenetical role of B lymphocytes in RA [5-9]. In several clinical trials B cell depletion with rituximab has been shown to be effective in treatment of RA and well tolerated by patients. Peripheral B cell depletion lasts usually 6-9 months. Recently a characteristic regeneration pattern of B cell subpopulations with a long lasting modulation of B cell subset composition has been reported [10, 11].
Regulatory T (Treg) cells represent a distinct subset of lymphocytes. They are attributed to have a key function in limiting immune responses against infectious agents and in avoiding pathologic autoimmunity. Defects in Treg function are discussed to play an important role in the pathophysiology of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [12, 13].
There are still different concepts in defining Treg [14-17]. The best described Treg population is thought to be CD4+CD25++. In addition to this, Tregs have been defined by the expression of CD4 and the transcription factor Foxp3. Foxp3 seems to be characteristically expressed by Tregs and plays an important role in development of Tregs. Recently, a new subset of CD4 and CD8 positive T cells has been reported, characterized by the constitutive expression of the immunotolerogenic molecule HLA-G [18]. Besides the membrane-bound isoforms, HLA-G can be secreted and is found at detectable levels in the peripheral blood. Both, membrane bound and soluble HLA-G levels have been linked to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and previous data suggest a positive correlation between soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients [19].
The role of Treg in RA is still not exactly defined [20-22]. Tregs from synovial fluid showed increased expression of activation markers like CTLA-4 (both surface and intracellular), GITR and OX40, as well as Foxp3 transcripts [23].
B cells have multiple effects on the T cell compartment. They directly interact with T cells during antigen presentation, produce cytokines and have specific functions for the organization of tertiary lymphoid structures like germinal center formation [24]. However, very little is known about the impact of B-cell depletion on peripheral T cell subpopulations. Particularly regulatory T cells are important candidates which may be indirectly influenced by rituximab treatment. In this study, four colour staining was performed using CD19, CD27, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD16, CD56, CD25, HLA-DR, HLA-G and intracellular Foxp3 to study the effects of B cell depletion mediated by rituximab on different subsets of T cells with particular interest in regulatory T cells. In addition, quantification of sHLA-G in sera of five patients has been performed.
MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY
Patient samples, patient characteristics, and study design.
Peripheral blood samples were obtained from 17 patients with RA, at the indicated time points whose B cell regeneration pattern has been published recently [11]. For immunfluorescence staining of Foxp3 peripheral blood samples were obtained from seven patients out of 17. Furthermore, in these seven patients HLA-G staining was performed and sHLA-G was determined in sera of five out of these seven patients. All patients met the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of RA. In all patients, RA was refractory to standard treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, including methotrexate (MTX) and/or tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists (etanercept, adalimumab or infliximab). Informed consent was obtained from all patients before entering the study, in accordance with the protocol approved by the ethics committee of the University of Wuerzburg. More than 70% (12 of 17) of patients continued to receive concomitant MTX. Rituximab was administered as follows: patients 1-6 received 4 weekly infusions of rituximab at a dose of 375 mg/m2 (range 2.4-3.6 gm); patients 7-17 received 2 infusions of 1,000 mg rituximab, 2 weeks apart. Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of the patients. Peripheral blood was collected from the patients at the time points before B cell depletion and 1-3, 4-6, 7-9 and 10-12 months after rituximab, respectively.
Characteristics of the Patients
| Characteristic | Baseline | 6 months | 12 months |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (range) years | 48 (28-77) | ||
| Female sex, % | 88 | ||
| Disease duration, mean (range) years | 11.4 (1-28) | ||
| Receiving MTX, % | 70.6 | ||
| RF positivity, % | 88 | ||
| DAS28 score, mean (range) | 6.1 (3.6-7.8) | 4.1 (3.0-6.9) | 4.9 (2.4-7.7) |
| RF, mean (range) IU/ml | 292.7 (17-1,180) | 110.5 (12-341) | 155.8 (12-617) |
| ESR, mean (range) mm/hour | 28 (12-38) | 15 (7-33) | 21 (8-46) |
| CRP, mean (range) mg/dl | 3.93 (0.6-10.4) | 0.79 (0.03-2.24) | 1.6 (0.09-5.9) |
| Before therapy | 6-8 months | 12-16 months | |
| CD19+ B cells/μl, mean (range) | 77 (43-335) | 16 (0-28) | 92 (11-132) |
MTX = methotrexate; RF = rheumatoid factor; DAS28 = Disease Activity Score in 28 joints; ESR = erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP = C-reactive protein; CD19+ B cells/μl in peripheral blood; n=17.
Time Course of T-Cell Subsets After B-Cell Depletion with Rituximab Compared to Baseline
| % | Before Therapy | 1-3 | 4-6 | 7-9 | 10-12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3+ | 66 ± 10 % | 74 ± 11 %* | 73 ± 12 %* | 73 ± 8 %* | 73 ± 8 %* |
| CD4+ | 47 ± 11 % | 55 ± 10 %* | 51 ± 9 %* | 51 ± 10 %* | 52 ± 9 %* |
| CD8+ | 26 ± 7 % | 25 ± 6 % | 28 ± 9 % | 27 ± 7 % | 26 ± 9 % |
| CD4+CD25+ | 23 ± 8 % | 24 ± 13 % | 22 ± 8 % | 20 ± 7 % | 20 ± 10 % |
| CD3+HLA DR+ | 6 ± 5 % | 6 ± 7 % | 6 ± 5 % | 5 ± 3 % | 5 ± 4 % |
| cells/microlitre | |||||
| CD3+ | 867 ± 537 | 951 ± 419 | 923 ± 404 | 996 ± 584 | 951 ± 624 |
| CD4+ | 630 ± 417 | 720 ± 299 | 642 ± 270 | 718 ± 474 | 689 ± 475 |
| CD8+ | 318 ± 176 | 304 ± 126 | 348 ± 161 | 350 ± 154 | 324 ± 215 |
| CD4+CD25+ | 314 ±196 | 298 ± 209 | 265 ± 121 | 248 ± 108 | 266 ± 232 |
| CD3+HLA DR+ | 69 ± 63 | 49 ± 25 | 75 ± 82 | 59 ± 30 | 61 ± 68 |
Relative frequency within lymphocytes and absolute numbers;mean ± SEM
* p < 0.05.
Cell preparation:
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were prepared by Ficoll-Paque Plus separation (Pharmacia Biotech, Freiburg, Germany).
Monoclonal antibodies:
For immunofluorescence staining, the following cell surface markers were used: CD19 (phycoerythrin [PE]), CD27 (phycoerythrin [PE]), CD3 (peridinin chlorophyll protein [PerCP]), CD4 (SK3, [PerCP]), CD8 (SK1, [APC]) from Becton Dickinson (Heidelberg, Germany); CD4 (fluorescein isothiocyanate [FITC]), CD8 (fluorescein isothiocyanate, [FITC]), HLA-DR (phycoerythrin [PE]) from Beckmann & Coulter; CD25 (allophycocyanin [APC]), CD56 ([PE]), CD16 ([PE]) from Becton Dickinson; anti-human Foxp3 ([PE]) from eBioscience (San Diego, USA); anti-human HLA-G (MEM-G/9, [PE], Exbio, Praha, Czech Republic), rat IgG2a (phycoerythrin [PE]) from ACRIS, rat IgG1 ([PE]) and mouse IgG1 ([PE], [PerCP] and [APC]) from Becton Dickinson.
Flow cytometric analysis:
Immunofluorescence staining for flow cytometric analysis was performed by incubating PBMCs in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 10 µl of monoclonal antibodies for 20 minutes on ice. In each tube, 1x106 cells were suspended. The cells were then washed in PBS. Immunfluorescence staining for Foxp3 was performed using a commercially available kit from eBioscience (San Diego, USA). Four-color staining was performed and followed by analysis using the FACSCalibur system (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA). T and B cells were identified by forward versus side scatter (FSC/SSC) gating on viable lymphocytes in combination with gating on CD19+ and CD3+ cells, respectively. A total of minimum 5,000 events were collected for each analysis. The frequency of cell populations was calculated using CellQuest software (Becton Dickinson). The total numbers of cells were calculated per millilitre of blood, based on the frequencies of these cells among lymphocytes and the white blood cell count.
For the analysis of HLA-G positive T cells gates were set on lymphocytes according to their characteristic properties in the FSC/SSC. Additional gates were set on FSC/CD4 or FSC/CD8 dot plots to identify the desired subsets. HLA-G expression was assessed in comparison to the respective isotype control staining. Due to the low frequency of HLA-G+ T cells at least 75.000 events in the lymphocyte gate were collected for each analysis.
Soluble HLA-G:
To quantify soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) in serum we used a commercially available ELISA Kit (Exbio, Praha, Czech Republic) with a lower limit of detection of 0.5 to 1 ng/millilitre according to the manufacturer's protocol. Serum samples were diluted 1 : 3 in PBS and ELISA was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All samples were run in duplicates. Cell culture supernatant of HLA-G5 transfected HeLA cells (kindly provided by E. Weiss, Munich) was used as an internal standard.
Statistical analysis:
Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired 2-tailed t-test with bonferroni correction. Values are expressed as the mean ± SEM and were calculated using Excel software and SPSS - software (Statistical Product and Service Solutions; SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA). P values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
B-Cell Compartment
After treatment with rituximab all patients showed a depletion of CD19+ B lymphocytes (to < 0.1%) in peripheral blood. Peripheral B cell depletion lasted 6 to 9 months after Rituximab (mean ± SEM 7.6 ± 0,6 months) [11]. The absolute numbers of CD19+ B lymphocytes returned to baseline levels 12 months after therapy (Table 1). Only 1 patient did not recover normal B cell numbers, and in that patient the levels remained reduced at 11.2 cells/μl. The numerically low B cell levels were not accompanied by a special clinical course or a different B cell regeneration pattern.
B cell depletion was accompanied by a significant clinical improvement regarding disease activity like decrease in tender and swollen joint count, CRP or ESR (data not shown).
T-Cell Compartment
The absolute number of CD3 positive lymphocytes showed no significant changes during the time of B cell depletion and during the regeneration phase up to 1 year after B cell depletion compared to before therapy (Table 2). The absolute numbers for CD4+ and CD8+ cells showed no significant changes either. Nevertheless we observed some changes in the composition of the peripheral lymphocyte pool. The relative frequency of CD3+ cells was significantly increased within 1-12 months after Rituximab (p < 0.05). This was related to a statistically significant increase of CD4+ T cells. CD8+ T cells did neither show significant changes in the absolute numbers nor in the relative frequency. For additional subtypes of T cells neither the relative frequency nor the absolute cell number changed significantly compared to the timepoint before therapy. This was found for CD3+HLA-DR+, CD3+CD16+ and/or 56+, CD3-CD16+ and/or 56+, CD8+CD25+, CD8+HLA-DR+, CD4+HLA-DR+ and CD3+γδ+ (data not shown).
CD4+CD25+ Compartment and Foxp3
Since regulatory T cells are thought to be more important for the pathophysiology of RA, we studied the CD4+CD25+ compartment more in detail. We did not observe any significant increase or decrease in the absolute numbers or the relative frequency of CD4+CD25+ cells (Table 2). In particular, also the percentage and absolute cell count for regulatory T cells defined as CD4+CD25++ T-cells remained constant over the period under review and did not show any statistically significant changes compared to the timepoint before administration of rituximab.
Next we studied Fox P3 positive CD4+ T cells. Both, the absolute number and the relative frequency of Fox P3 positive T-cells did not change statistically significant over the period under review (Fig. 1).
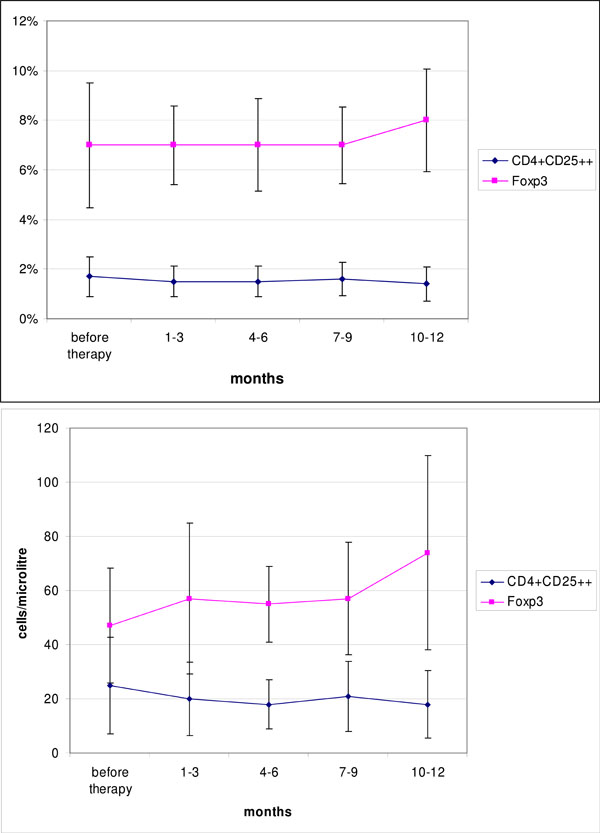
Time course of CD4+CD25++ and Foxp3 positive T cells (relative frequency within lymphocytes, Foxp3 within CD4+ lymphocytes) and absolute numbers after B-cell depletion with rituximab compared to baseline. (mean ± SEM).

Mean frequencies of CD4+HLA-G+ and CD8+HLA-G+ as percentages of CD4+ or CD8+ respectively at different time points during the first year follow up after initiation of rituximab treatment. (mean ± SEM, n=7).
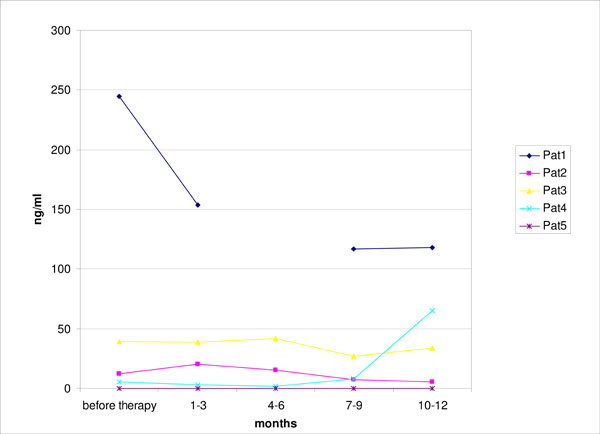
Serum levels of sHLA-G during the first year of follow-up after initiation of rituximab therapy as measured by ELISA. (n=5).
HLA-G
HLA-G defines a novel subset of regulatory T cells. Therefore we studied the numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ HLA-G+ cells under rituximab treatment. Before initiating rituximab an average of 0.95% of CD4+ T cells in the peripheral blood of RA patients expressed HLA-G (range 0.6% to 1.7%, n=7). Analysis of HLA-G expression on CD8 revealed an average of 1.56 % HLA-G positive CD8+ T cells in RA patients (range 0.9% to 3.6%, n= 7). Although the frequency of CD4+HLA-G+ and CD8+HLA-G+ varied in between the different time points in single patients we could not find a significant change for these subpopulations (Fig. 2). The absolute cell counts did not show significant changes neither for CD4+HLA-G+ nor CD8+HLA-G+ (data not shown).
sHLA-G
Serum levels of sHLA-G were previously found to be decreased in RA patients and have been linked to disease activity [12]. However, we did not observe a consistent significant change in soluble HLA-G as measured by ELISA in the sera of five patients under rituximab treatment during the first year of follow-up (Fig. 3).
DISCUSSION
Both, B and T cells have been shown to be of crucial importance in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders e.g. RA [2, 5, 25]. B cell depletion by rituximab has been approved for treatment of severe RA refractory to conventional DMARDs including TNFalpha inhibitors in combination with methotrexate underlining the key function of B cells in the pathogenesis in RA [3, 4, 7, 9, 26-28]. Undoubtedly there is a linkage between the B and T cell compartment under both physiological and pathological conditions. B cells e.g. support the activation of T cells by expressing costimulatory molecules such as CD80/86 and CD40 or by the secretion of cytokines. Furthermore they function as antigen presenting cells and have essential effects on other cells required for the development of tertiary lymphoid tissues [24]. Rituximab treatment causes a profound peripheral B cell depletion which can be observed usually for about 6 months. In addition it causes dramatic changes in the homeostasis of B cell subsets which can be observed for more than a year after rituximab treatment [10, 11, 27, 29-31].
There is also evidence for a disturbed T cell homoeostasis within autoimmune diseases, in particular, a disturbance of T cells with immunosuppressive and regulatory function [12]. Several subsets of T cells with suppressive and regulatory functions have been described within the last years. To date, only 2 populations of “natural” regulatory T cell populations can be identified in peripheral blood. 1) the population of CD4+CD25++ coexpressing Foxp3 and 2) the recently identified HLA-G-expressing CD4 or CD8 Tregs.
Valencia et al. demonstrated differences regarding the expression of Foxp3 in patients with SLE [32]. In rheumatoid arthritis, Mottonen et al. studied the characteristics of CD4+CD25+ T cells in peripheral blood (PB) and synovial fluid (SF) compared to normal controls [23]. They found an increased frequency of CD4+ cells T cells expressing CD25 in SF compared to PB from patients with RA. However, no significant difference was observed in the numbers of CD4+CD25+ T cells in PB from patients and controls.
There is evidence that CD4+CD25++Foxp3+ T regs are modulated by anti-TNF therapies [33]. CD4+CD25++ Tregs isolated from patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) expressed reduced levels of Foxp3 mRNA and protein which was ameliorated by inhibition of TNFalpha with infliximab [34]. In another study, treatment with infliximab also restored the capacity of regulatory T cells to inhibit cytokine production and to induce a suppressive phenotype on CD4+CD25- T cells [35]. Furthermore, anti-TNFalpha treatment led to a significant rise in the number of peripheral blood regulatory T cells in RA patients responding to this treatment. These data so far suggest that particularly regulatory T cells are of importance also for RA, which can be influenced to a certain extent by antiinflammatory treatment.
Only little is known about the influence of rituximab mediated B-cell depletion on the T-cell compartment and in particular on regulatory T-cells.
Leandro et al. could not find significant changes in the frequency and absolute number of T cells (CD3+) and NK cells (CD3-CD56+) at 1 month and 3 months after rituximab in RA. In addition, no significant differences were detected in the different subpopulations of T cells like CD4+, CD8+ and CD4+ T cells expressing CD25 [10]. Since the clinical response to rituximab is somewhat delayed and not yet fully developed at 3 months after rituximab and B cell homeostasis is disturbed for more than a year, changes in the T cell compartment may also evolve later than three months after Rituximab. Therefore we extended these data by analysing T cell subpopulation over a period of one year. Both, the relative frequency and also the absolute number of CD4+CD25++ T cells in our population remained constant without any significant changes. Despite the fact that we saw a significant increase in the relative frequency of CD3+ cells and in the CD4+ subset within 1-12 months after Rituximab (p < 0.05), the absolute numbers of CD3+ and CD4+ T cells as well as CD3+HLA-DR+, CD3+CD16/56+, CD8+CD25+, CD8+HLA-DR+, CD4+HLA-DR+ and CD3+γδ+ and of NK cells (CD3-CD56+) were not significantly altered. This can be explained by the lack or reduced levels of B-cells during period under review, respectively. Due to extensive pretreatment before Rituximab investigated patients in our study tended to have low lymphocyte counts. As a consequence absolute numbers of T cells were generally low.
Of particular interest was the analysis of the Treg compartment. In the study by Leandro the frequency of CD4+CD25++ T cells decreased 1 month after treatment significantly (p < 0.05), but the total numbers did not, and no significant differences were found at 3 months. In our population we could not find a decrease in the frequency of CD4+CD25++ within 3 months after Rituximab. However, we did not specifically look within the first 4 weeks after rituximab since we thought this period to be confounded by the i.v prednisolone used during antibody infusions. The relative frequency and also the absolute number of CD4+CD25++ T cells remained constant without any significant changes up to one year after initiating B cell depletion. Also the numbers of Foxp3+CD4+ T cells remained constant under rituximab treatment. In lupus nephritis Sfikakis et al. could show increased Foxp3 mRNA after B cell depletion by Rituximab in peripheral blood of 7 patients [36]. During follow-up, increased Foxp3 mRNA persisted in those patients in clinical remission, while in those patients with active disease subsequent decreases were noted. It is not clear whether the different techniques for defining Foxp3+ Treg or the different pathophysiology between RA and lupus accounts for these differences.
An interesting new subset of regulatory T cells which does not share the CD25++ Foxp3 phenotype are the HLA-G expressing Treg. HLA-G expressing T cells represent a novel subset of natural occurring regulatory T cells, that efficiently inhibit autologous T cell proliferation via a yet to be defined cell-contact independent mechanism. HLA-G positive T cells can be found at low percentages in the peripheral blood of healthy volunteers and the presence of HLA-G+ T cells at sites of inflammation due to infections or autoreactivity like neuroinflammatory disorders (e.g. multiple sclerosis, vasculitis, encephalitis or myositis) suggests an important function of these cells in modulating inflammatory responses in vivo [37, 38]. Similar to membrane bound HLA-G on T cells Verbruggen et al. were able to demonstrate that soluble HLA-G was lower in RA but positively correlated with parameters of RA disease activity [19]. However, we did not observe a consistent significant change in soluble HLA-G as measured by ELISA in the sera of five patients under rituximab treatment.
From our data, there seems to be no evidence for any numerical influence of CD20 mediated B cell depletion on the amounts and frequency of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood in RA. For future studies it will be relevant to extend the analysis of Tregs to their function, since the available data give no indication whether B cell depletion is able to restore defective regulatory T cell activity. Results regarding T cell subsets after B cell depletion via Rituximab may also vary depending on the underlying disease. To address this, there is an obvious need for further studies on the impact of therapeutic B cell depletion on T cell subsets.
CONCLUSION
Our data for patients with RA indicate that absolute T cell counts do not change significantly after rituximab compared to the time before therapy for all studied populations in peripheral blood. In particular, the frequency and the absolute number of regulatory T cells defined as T cells characterized by CD4+/CD25++, Fox P3 or HLA-G expression were numerically stable during transient B-cell depletion using anti-CD20 antibodies up to 12 months in the peripheral blood.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Isabella Kuntzsch and Kathrin Zehe for technical assistance and the IZKF of the University of Würzburg for funding.


